Difference between revisions of "DWDM"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''DWDM''' stands for '''d'''ense '''w'''avelength '''d'''ivision '''m'''ultiplexing | '''DWDM''' stands for '''d'''ense '''w'''avelength '''d'''ivision '''m'''ultiplexing | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a technology that puts data from different sources together on an optical fiber, with each signal carried at the same time on its own separate light wavelength. DWDM is using, up to 80 (and theoretically more) separate wavelengths or channels of data can be multiplexed into a lightstream transmitted on a single optical fiber. Each channel carries a time division multiplexed (TDM) signal. All colors are 0,8nm broad. Therforce, they must be cooled, that the distance between the colors are constant. | Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a technology that puts data from different sources together on an optical fiber, with each signal carried at the same time on its own separate light wavelength. DWDM is using, up to 80 (and theoretically more) separate wavelengths or channels of data can be multiplexed into a lightstream transmitted on a single optical fiber. Each channel carries a time division multiplexed (TDM) signal. All colors are 0,8nm broad. Therforce, they must be cooled, that the distance between the colors are constant. | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| − | '''Difference to CWDM | + | =='''Difference to CWDM'''== |
* larger range | * larger range | ||
* more colors | * more colors | ||
| Line 13: | Line 11: | ||
* active | * active | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| − | '''DWDM operating mode:''' | + | =='''DWDM operating mode:'''== |
| − | |||
At first, you need pro color a GBIC, a SFP, a XFP or a XENPAK. Then you will connect your optical transceiver with a MUX. This device bunch your signal an send it over one fiberoptic cable to a DEMUX. This device will split the signal in the original state and send it to the optical transceiver back | At first, you need pro color a GBIC, a SFP, a XFP or a XENPAK. Then you will connect your optical transceiver with a MUX. This device bunch your signal an send it over one fiberoptic cable to a DEMUX. This device will split the signal in the original state and send it to the optical transceiver back | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
[[Image:dwdm.jpg]] | [[Image:dwdm.jpg]] | ||
| − | + | <br/><br/> | |
| − | '''Cisco DWDM XENPAK Product Information''' | + | =='''Cisco DWDM XENPAK Product Information'''== |
{| border = "1" | {| border = "1" | ||
||'''Product Number''' | ||'''Product Number''' | ||
| Line 159: | Line 156: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| − | '''Cisco DWDM SFP Product Information''' | + | =='''Cisco DWDM SFP Product Information'''== |
{| border = "1" | {| border = "1" | ||
||'''Product Number''' | ||'''Product Number''' | ||
| Line 327: | Line 324: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| − | '''Cisco DWDM X2 Ordering Information''' | + | =='''Cisco DWDM X2 Ordering Information'''== |
{| border = "1" | {| border = "1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 464: | Line 461: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| − | '''Cisco DWDM GBIC Product Information''' | + | =='''Cisco DWDM GBIC Product Information'''== |
{| border = "1" | {| border = "1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 14:17, 23 July 2009
DWDM stands for dense wavelength division multiplexing
Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a technology that puts data from different sources together on an optical fiber, with each signal carried at the same time on its own separate light wavelength. DWDM is using, up to 80 (and theoretically more) separate wavelengths or channels of data can be multiplexed into a lightstream transmitted on a single optical fiber. Each channel carries a time division multiplexed (TDM) signal. All colors are 0,8nm broad. Therforce, they must be cooled, that the distance between the colors are constant.
Difference to CWDM
- larger range
- more colors
- faster
- expensive, because the laser are cooled
- smaler distance between the "colors", only 0,8nm
- active
DWDM operating mode:
At first, you need pro color a GBIC, a SFP, a XFP or a XENPAK. Then you will connect your optical transceiver with a MUX. This device bunch your signal an send it over one fiberoptic cable to a DEMUX. This device will split the signal in the original state and send it to the optical transceiver back
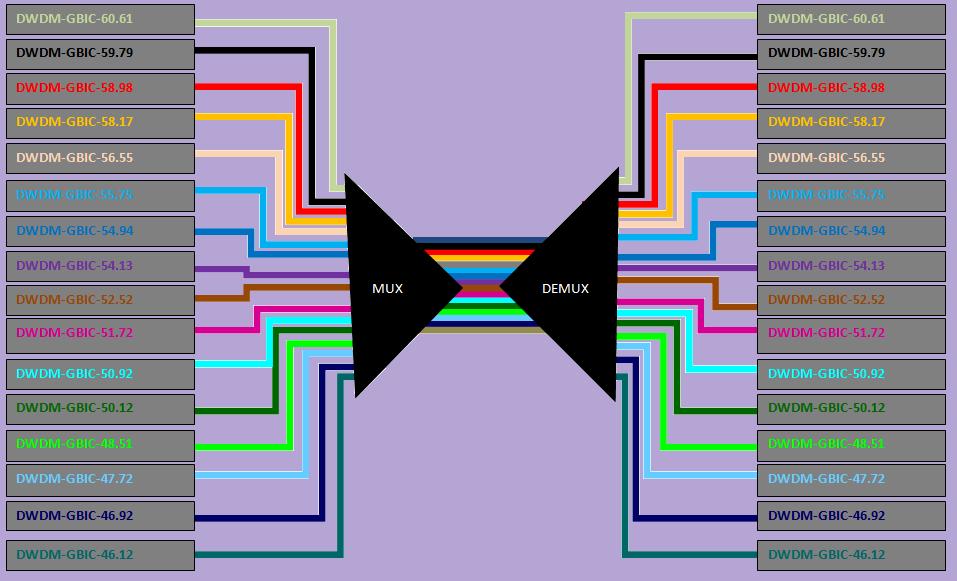
Cisco DWDM XENPAK Product Information
| Product Number | Description | ITU Channel |
| DWDM-XENPAK-60.61= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1560.61 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 21 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-59.79= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1559.79 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 22 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-58.98= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1558.98 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 23 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-58.17= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1558.17 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 24 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-56.55= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1556.55 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 26 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-55.75= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1555.75 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 27 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-54.94= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1554.94 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 28 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-54.13= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1554.13 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 29 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-52.52= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1552.52 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 31 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-51.72= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1551.72 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 32 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-50.92= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1550.92 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 33 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-50.12= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1550.12 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 34 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-48.51= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1548.51 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 36 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-47.72= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1547.72 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 37 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-46.92= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1546.92 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 38 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-46.12= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1546.12 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 39 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-44.53= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1544.53 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 41 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-43.73= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1543.73 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 42 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-42.94= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1542.94 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 43 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-42.14= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1542.14 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 44 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-40.56= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1540.56 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 46 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-39.77= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1539.77 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 47 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-38.98= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1538.98 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 48 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-38.19= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1538.19 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 49 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-36.61= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1536.61 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 51 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-35.82= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1535.82 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 52 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-35.04= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1535.04 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 53 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-34.25= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1534.25 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 54 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-32.68= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1532.68 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 56 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-31.90= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1531.90 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 57 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-31.12= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1531.12 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 58 |
| DWDM-XENPAK-30.33= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1530.33 nm XENPAK (100-GHz ITU grid) | 59 |
| WDM-XENPAK-REC= | 10GBASE-WDM receive-only XENPAK |
Cisco DWDM SFP Product Information
| Product Number | Description | ITU Channel |
| DWDM-SFP-6141 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1561.42 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 20 |
| DWDM-SFP-6061= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1560.61 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 21 |
| DWDM-SFP-5979= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1559.79 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 22 |
| DWDM-SFP-5898= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1558.98 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 23 |
| DWDM-SFP-5817= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1558.17 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 24 |
| DWDM-SFP-5736= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1557.36 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 25 |
| DWDM-SFP-5655= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1556.55 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 26 |
| DWDM-SFP-5575= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1555.75 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 27 |
| DWDM-SFP-5494= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1554.94 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 28 |
| DWDM-SFP-5413= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1554.13 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 29 |
| DWDM-SFP-5332= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1553.33 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 30 |
| DWDM-SFP-5252= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1552.52 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 31 |
| DWDM-SFP-5172= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1551.72 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 32 |
| DWDM-SFP-5092= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1550.92 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 33 |
| DWDM-SFP-5012= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1550.12 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 34 |
| DWDM-SFP-4931= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1549.32 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 35 |
| DWDM-SFP-4851= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1548.51 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 36 |
| DWDM-SFP-4772= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1547.72 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 37 |
| DWDM-SFP-4692= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1546.92 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 38 |
| DWDM-SFP-4612= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1546.12 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 39 |
| DWDM-SFP-4532= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1545.32 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 40 |
| DWDM-SFP-4453= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1544.53 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 41 |
| DWDM-SFP-4373= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1543.73 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 42 |
| DWDM-SFP-4294= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1542.94 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 43 |
| DWDM-SFP-4214= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1542.14 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 44 |
| DWDM-SFP-4134= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1541.35 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 45 |
| DWDM-SFP-4056= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1540.56 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 46 |
| DWDM-SFP-3977= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1539.77 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 47 |
| DWDM-SFP-3898= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1538.98 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 48 |
| DWDM-SFP-3819= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1538.19 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 49 |
| DWDM-SFP-3739= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1537.40 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 50 |
| DWDM-SFP-3661= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1536.61 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 51 |
| DWDM-SFP-3582= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1535.82 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 52 |
| DWDM-SFP-3504= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1535.04 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 53 |
| DWDM-SFP-3425= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1534.25 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 54 |
| DWDM-SFP-3346= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1533.47 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 55 |
| DWDM-SFP-3268= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1532.68 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 56 |
| DWDM-SFP-3190= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1531.90 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 57 |
| DWDM-SFP-3112= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1531.12 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 58 |
| DWDM-SFP-3033= | 1000BASE-DWDM 1530.33 nm SFP (100-GHz ITU grid) | 59 |
Cisco DWDM X2 Ordering Information
| Product Number | Description | ITU Channel |
| DWDM-X2-60.61= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1560.61 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 21 |
| DWDM-X2-59.79= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1559.79 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 22 |
| DWDM-X2-58.98= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1558.98 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 23 |
| DWDM-X2-58.17= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1558.17 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 24 |
| DWDM-X2-56.55= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1556.55 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 26 |
| DWDM-X2-55.75= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1555.75 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 27 |
| DWDM-X2-54.94= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1554.94 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 28 |
| DWDM-X2-54.13= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1554.13 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 29 |
| DWDM-X2-52.52= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1552.52 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 31 |
| DWDM-X2-51.72= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1551.72 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 32 |
| DWDM-X2-50.92= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1550.92 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 33 |
| DWDM-X2-50.12= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1550.12 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 34 |
| DWDM-X2-48.51= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1548.51 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 36 |
| DWDM-X2-47.72= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1547.72 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 37 |
| DWDM-X2-46.92= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1546.92 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 38 |
| DWDM-X2-46.12= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1546.12 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 39 |
| DWDM-X2-44.53= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1544.53 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 41 |
| DWDM-X2-43.73= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1543.73 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 42 |
| DWDM-X2-42.94= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1542.94 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 43 |
| DWDM-X2-42.14= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1542.14 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 44 |
| DWDM-X2-40.56= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1540.56 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 46 |
| DWDM-X2-39.77= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1539.77 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 47 |
| DWDM-X2-38.98= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1538.98 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 48 |
| DWDM-X2-38.19= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1538.19 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 49 |
| DWDM-X2-36.61= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1536.61 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 51 |
| DWDM-X2-35.82= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1535.82 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 52 |
| DWDM-X2-35.04= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1535.04 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 53 |
| DWDM-X2-34.25= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1534.25 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 54 |
| DWDM-X2-32.68= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1532.68 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 56 |
| DWDM-X2-31.90= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1531.90 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 57 |
| DWDM-X2-31.12= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1531.12 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 58 |
| DWDM-X2-30.33= | 10GBASE-DWDM 1530.33 nm X2 (100-GHz ITU grid) | 59 |
Cisco DWDM GBIC Product Information
| Product Number | Description | ITU Channel |
| DWDM-GBIC-60.61 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1560.61 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 21 |
| DWDM-GBIC-59.79 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1559.79 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 22 |
| DWDM-GBIC-58.98 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1558.98 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 23 |
| DWDM-GBIC-58.17 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1558.17 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 24 |
| DWDM-GBIC-56.55 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1556.55 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 26 |
| DWDM-GBIC-55.75 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1555.75 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 27 |
| DWDM-GBIC-54.94 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1554.94 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 28 |
| DWDM-GBIC-54.13 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1554.13 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 29 |
| DWDM-GBIC-52.52 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1552.52 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 31 |
| DWDM-GBIC-51.72 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1551.72 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 32 |
| DWDM-GBIC-50.92 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1550.92 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 33 |
| DWDM-GBIC-50.12 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1550.12 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 34 |
| DWDM-GBIC-48.51 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1548.51 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 36 |
| DWDM-GBIC-47.72 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1547.72 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 37 |
| DWDM-GBIC-46.92 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1546.92 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 38 |
| DWDM-GBIC-46.12 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1546.12 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 39 |
| DWDM-GBIC-44.53 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1544.53 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 41 |
| DWDM-GBIC-43.73 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1543.73 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 42 |
| DWDM-GBIC-42.94 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1542.94 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 43 |
| DWDM-GBIC-42.14 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1542.14 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 44 |
| DWDM-GBIC-40.56 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1540.56 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 46 |
| DWDM-GBIC-39.77 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1539.77 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 47 |
| DWDM-GBIC-38.98 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1538.98 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 48 |
| DWDM-GBIC-38.19 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1538.19 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 49 |
| DWDM-GBIC-36.61 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1536.61 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 51 |
| DWDM-GBIC-35.82 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1535.82 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 52 |
| DWDM-GBIC-35.04 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1535.04 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 53 |
| DWDM-GBIC-34.25 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1534.25 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 54 |
| DWDM-GBIC-32.68 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1532.68 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 56 |
| DWDM-GBIC-31.90 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1531.90 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 57 |
| DWDM-GBIC-31.12 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1531.12 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 58 |
| DWDM-GBIC-30.33 | 1000BASE-DWDM 1530.33 Nm GBIC (100 GHz ITU grid) | 59 |